What Are The Symptoms Of Diabetes In Women? Diabetes is a metabolic disease that occurs when the human body has high blood sugar as a result of problems with insulin regulation or production. Diabetes, also known as diabetes, can occur in everyone, regardless of age, race, gender, or lifestyle.
Diabetes in women can be a little more problematic. Pancreatic cells, which can secrete enough insulin before pregnancy, cannot secrete enough insulin as pregnancy progresses, so blood sugar levels can rise during pregnancy, even though there are no signs of diabetes before.
Generally, people with a large number of diabetics in their family, over the age of 30, overweight pregnant women are at risk of gestational diabetes. Gestational diabetes usually improves after birth, but the risk of recurrence in subsequent pregnancies is high.
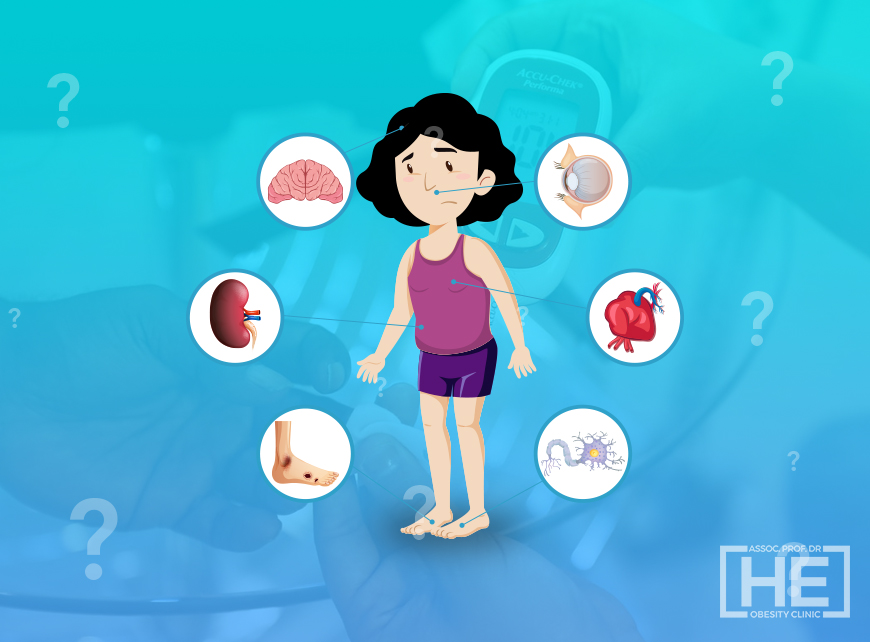
Typical symptoms of diabetes caused by an imbalance in blood sugar are drinking a lot of water, being very hungry, and urinating frequently. In addition, loss of appetite, weakness, rapid fatigue, blurred vision, unexplained weight loss, itching, stubborn infections, and many other signs can be symptoms of diabetes.
The patient may experience symptoms associated with diabetes damage to the body. A person with diabetes should be able to recognize his disease and the medications he is using well and produce urgent solutions when necessary, take responsibility for managing the disease. For this, he also needs adequate education about his disease and strict communication with health professionals
Diabetes in Women
The amount of sugar in the blood of diabetes patients increases and is expelled from the kidneys. Diabetes, which occurs when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin hormone or the insulin hormone it produces cannot be used effectively, can also be seen in a newborn baby and in an 80-year-old person.
Diabetes, which is becoming more common all over the world along with the sedentary lifestyle that comes with urbanization, the wrong eating habit, is often accompanied by obesity.
It is most common in people in middle age and older. As a result of inaccuracies in eating habits, an increase in the incidence of obesity in children and young adults in recent years can lead to the age of onset of diabetes.
Diabetes in women is more risky. Because during pregnancy, very serious problems can occur. The appearance of one or more of the symptoms of diabetes in women may not always be a sign of diabetes.
These symptoms can also be seen routinely or as a symptom of other diseases. But you should not take risks in this regard. If the symptoms in question are intense and frequent, a doctor should be consulted. The earlier diabetes is diagnosed, the easier the treatment will be.
How does diabetes affect a woman?
Diabetes mellitus, which leads to damage to the heart and vessels, also negatively affects sexual life. In men, sexual aversion, ejaculation problems and erection problems occur, while in women, vaginal dryness, sexual aversion and genital infections trigger.
It causes many problems in female patients, such as sexual problems, in which diabetes is effective in male patients. In particular, sexual aversion and dryness of the vagina are among the most disturbing problems for women in the period of illness.
When women’s diabetes cannot be controlled, it causes serious painful periods to occur during sexual intercourse over time at the beginning of sexual problems.
Over time, sexual problems caused by diabetes in women can seriously disrupt the lives of patients as a result of urinary tract and vaginal infections. The main reason for the progression of such sexual problems in women is the inability to diagnose the disease early.
Symptoms of Diabetes in Women
Diabetes in women is different than in men. Symptoms of Diabetes in women are as follows:
- Vaginal infections and Thrush
As a result of too much development of yeast caused by the Candida fungus, it can lead to infections and vaginal thrush in the area. These ailments are common in women.
When the infection occurs in the vaginal part, it is manifested by symptoms such as itching, pain, discharge and painful sexuality. High glucose levels in the blood affect the development of this fungus.
- Urinary Tract Infections
It has been observed that women with diabetes have a greater risk of urinary tract disorders. When bacteria form in the urinary tract, this infection can lead to pain, burning sensation, bloody or blurred urine when urinating. Kidney diseases can also occur if steps are not taken for treatment.
- Decreased Sexual Urges
The condition that occurs when high blood sugar damages nerve fibers is diabetic neuropathy. Although this includes the feet, hands and legs, it can lead to tingling and loss of sensation in many parts of the body. It also creates numbness in the vaginal area, while at the same time reducing sexual urges.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
This disease occurs when the body produces more testosterone than the ideal level. Irregular periods, weight gain, acne and a depressed mood are among the symptoms of this disease.
In addition, it can lead to some form of insulin resistance and infertility. This, in turn, leads to the development of diabetes by raising blood sugar levels.
Common symptoms in both sexes are as follows ; needs water and increased hunger, more urination, weight loss or gain, fatigue, blurred vision, delayed healing of wounds, nausea, inflammations of the skin, dark spots, irritability, sweet, fruity, or acetone in the form of breath, slight numbness in your hands or feet. Type 2 diabetes, which has no definite symptoms, is a condition that proceeds insidiously.
- Pregnancy and Type 1/Type 2 diabetes
Some women with diabetes wonder whether pregnancy is dangerous. Being diagnosed with Type 1 or type 2 diabetes does not affect your health during pregnancy, but it is still useful to take precautions.
If you are planning to have children, it is best to maintain the balance of your blood sugar level before you become pregnant.
If you have diabetes and are pregnant, consult your doctor to ensure that you and your baby are healthy. For example, your blood sugar and health status in general should be monitored regularly before and during pregnancy.
When pregnant, blood sugar and ketones reach the baby. Babies get energy from glucose. However, when glucose levels are too high, the likelihood of problems and defects in the baby during birth increases. Transmission of high blood sugar to infants can lead to cognitive disorders and hypertension.
- Gestational diabetes (pregnancy-related diabetes)
Gestational diabetes, which is not the same as Type 1 and type 2 diabetes, is specific to pregnant women and occurs in about 9.2 percent of pregnancies.
Pregnancy hormones, which interfere with the body’s insulin production, lead the body to produce more insulin. It can also be the opposite, insulin produced on behalf of some women may still not be sufficient, and they may develop gestational diabetes.
What are the early and later diabetes signs in women?
Knowing the symptoms of diabetes provides the possibility of diagnosis and treatment in the early stages of the disease. The initial complaints of Type I diabetes, that is, diabetes that begins in children and teenagers, are very obvious.
In Type II diabetes, which begins at a later age, the symptoms are not always obvious. Thirst, drinking a lot of water, dry mouth, urinating a lot, the desire to urinate at night and excessive appetite may not be seen in every patient.
Some patients’ say they have been eating too much for years because they already have an excessive appetite. A variety of causes can trigger the disease in people at risk for diabetes. These include excessive emotional load, other expressions of great sadness or joy, vascular events such as surgery, infarction, and infections.